Master Planning
What is Master Planning?
Master Planning is the augmentation of information developed during the Facility and Process Planning phases. Starting with the refinement of the process plan and facility plan, it also may include development of preliminary site plan information. Major building utility systems—such as HVAC, refrigeration, and electrical—are also quantified in order to develop building and process utility requirements.
How is a Master Plan Developed?
-
Building materials and room finishes
-
Process equipment details
-
Room environments and types of heating, cooling, and refrigeration systems
-
Process equipment utility needs, such as boilers, chillers, compressed air, and electric
-
Cleaning and sanitation systems
What Does a Master Plan Look Like?
Elements of a Master Plan may include the following:
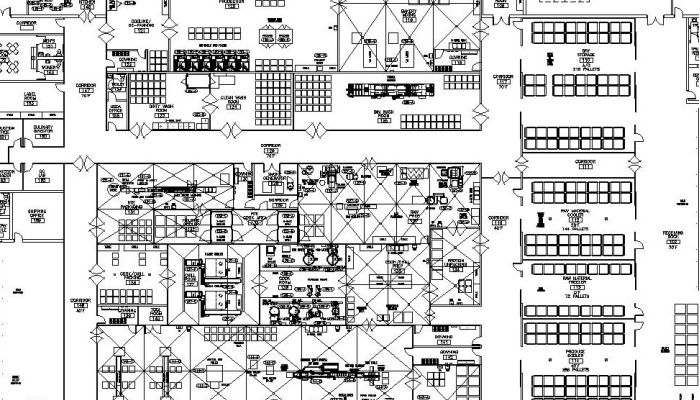
Process Floor Plan
Drawings showing process equipment, walls/openings, structural elements, materials/finishes, and a preliminary building code review.
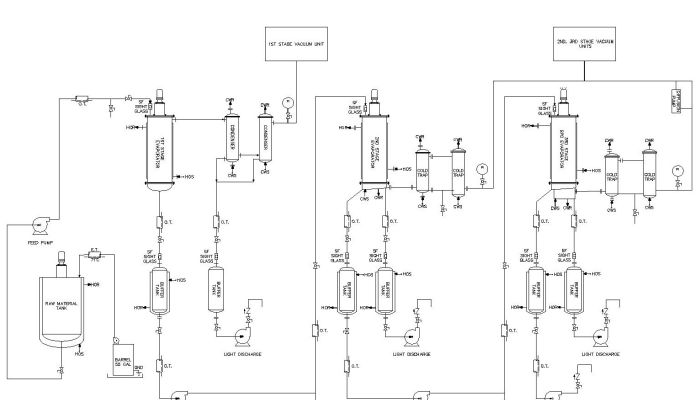
Process Flow Diagrams
Diagrams showing the process flow and equipment lists indicating make and model
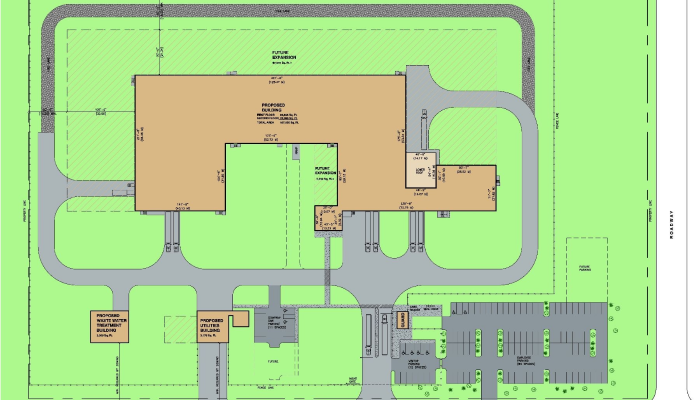
Site Plan
Preliminary site plan indicating roadways, parking, utilities, and future expansion opportunities.
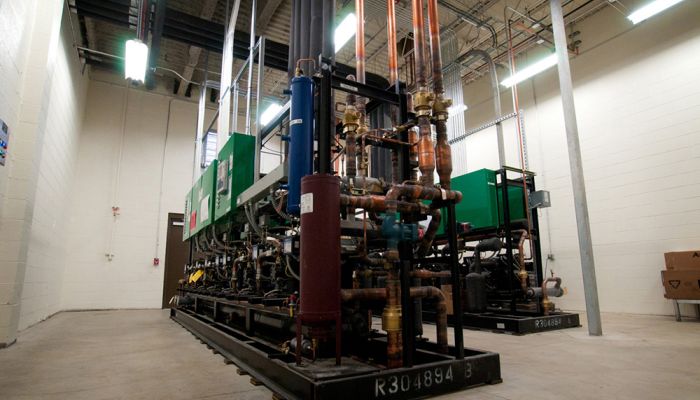

Mechanical and Electrical Systems
Systems to be utilized for heating, cooling, ventilating, refrigerating, and powering the building

Project Timeline
Primary project milestones for design, permitting, costing, and construction.

Project Cost
Costs for implementing the project segregated by area type or function, construction trades, or other relevant factors.

Utility Information
Capacity or usage estimates for water, gas, electric, and sewer systems.

Staffing Needs
Staffing needs to operate the facility including production, warehouse, maintenance, quality, sanitation and supervisors.

Phasing Options
Plans for phasing the project, including current implementation plans and future growth concepts.